이 포스팅은 총 4부로 이어지며 현재는 2부입니다.
- 1부 : Android, MVC, MVVM, MVP
- 2부 : Android 와 Annotation
- 3부 : AndroidAnnotations 과 MVC
- 4부 : AndroidAnnotations 과 테스트
Annotation 이란?
사전적 의미 : 주석
- 특정 클래스, 변수,메소드 등에 붙이는 코드로 해당 타겟의 기능을 좀 더 명확하게 해주는 역할을 합니다. Web Spring 프레임워크 등에서는 타겟의 기능을 정의하여 특정 역할을 수행할 수 있도록 사용되고 있습니다.
Java 에서 Annotation 이 동작하는 방식은 크게 2가지 입니다.
- java.lang.reflection 을 이용해서 Class 정보를 읽어 Instance 의 타겟에 Annotation 에 해당되는 기능을 정의하는 방식
- Annotation Processing Tool(APT) 을 이용하여 Compile 단계에서 Annotation 이 정의된 타겟의 정보를 미리 정의하는 방식
위의 2가지 방식 중에서는 2의 방식이 성능면에서 좋은 방식입니다. 하지만 APT 에 의한 방식은 Compile 된 클래스가 A.class -> A_.class 라는 식으로 “_” 가 붙는 단점이 있습니다.
Java Annotation 접근
- java.lang.reflection 을 이용한 동작
다음 코드는 java.lang.reflection 을 통해서 특정 타겟에 접근하여 객체에 Annotation 에 맞게 정의하는 방식입니다. (View 의 DI 를 위한 동작입니다.)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ResourceView {
int id() default 0;
}public class InjectController {
public static void injectLayout(Activity mActivity) {
Annotation[] annotations;
AbstractInjectCommand command;
ResourceLayout mLayoutAnnotation = mActivity.getClass().getAnnotation(ResourceLayout.class);
command = InjectFactory.createInjectCommand(mActivity, mLayoutAnnotation);
if (command != null) {
command.excute(null);
}
// 어노테이션이 선언된 타겟에 접근하기 위해 클래스 변수에 접근
Field[] fields = mActivity.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
int fieldSize = fields.length;
int annoSize;
Field field;
for (int fieldIdx = 0; fieldIdx < fieldSize; ++fieldIdx) {
field = fields[fieldIdx];
// private 변수에 접근하기 위함
field.setAccessible(true);
// 어노테이션 접근
annotations = field.getDeclaredAnnotations();
annoSize = annotations.length;
for (int annoIdx = 0; annoIdx < annoSize; ++annoIdx) {
// 어노테이션별 동작 수행
command = InjectFactory.createInjectCommand(mActivity, annotations[annoIdx]);
if (command != null) {
command.excute(field);
}
}
}
}
}Annotation 이 정의된 타겟을 Java Reflection 을 이용해서 접근한 뒤 Annotation 정보를 추출 후 Annotation 에 맞게 동작을 합니다. 위의 소스는 View 를 Binding 하는 과정 중 일부입니다.
- Annotation Processing Tool(APT) 에 의한 동작
이와 다르게 APT 를 이용한 방식은 Compile 단계에서 미리 Annotation 이 정의 되기 때문에 Compile 되는 순서를 도식화 하였습니다.
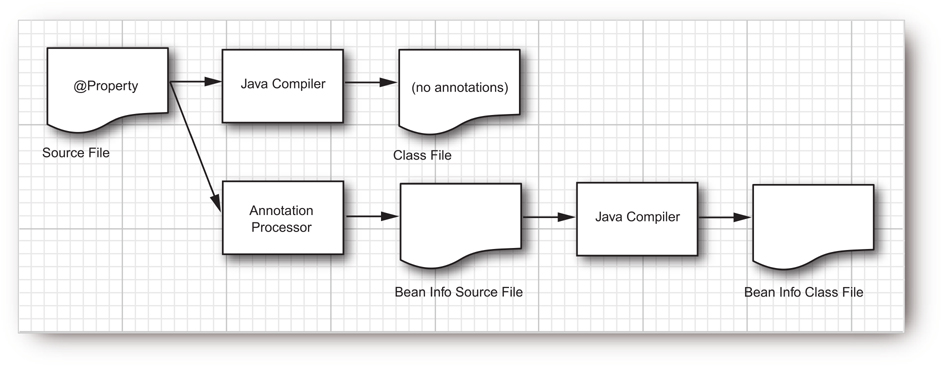 |
| http://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=2027052&seqNum=6 |
APT 는 컴파일 시점에 Java 코드 내의 Annotation 을 감지해서 Annotation 이 설정되어 있는 코드들은 새로운 Java 코드를 생성한 뒤 컴파일하도록 합니다.
Compile 단계가 더 추가되었지만 Runtime 시에는 성능상으로 영향이 거의 없다는 장점이 있습니다.
- java.lang.reflection? Annotation Processing Tool?
Replection 을 활용한 방법은 APT 에 대한 학습에 비하면 다소 쉬운면이 있습니다. 하지만 Runtime 시에 annotation 분석을 하기 때문에 성능상 이슈가 있습니다. 반면 APT 를 활용한 방식은 컴파일시 시간적인 비용과 APT 를 통해 생성된 코드는 A.java -> A_.java 와 같은 형태로 변한다는 단점이 있으나 Runtime 시 성능상 이점이 있습니다.
Android 와 Annotation
안드로이드에서는 기본적으로 Java 1.6 에서 사용되는 Annotation 들을 지원합니다. 대표적으로 @Override 입니다.
그외 에도 안드로이드 특성에 맞게 android.annotation 이 있으며 android.support.annotation 을 사용하면 Compile 시의 타겟에 대한 Validation을 미리 설정할수 있도록 도와줍니다.
그외에도 AndroidAnnotations, ButterKnife, Dagger 등이 APT 를 이용하여 안드로이드를 지원하고 있으며 안드로이드용 ORM 라이브러리는 java.lang.reflection 을 이용하여 동작합니다.

